Broadcom ($AVGO) Deep Dive: Where AI and Hyperscalers Converge
Broadcom Investment Thesis: why AVGO continues to lead the semiconductor revolution...
Hi, Investor 👋
I’m Jimmy, and welcome to another edition of our newsletter. Today, we’re diving into Broadcom ($AVGO) - a company at the heart of the AI boom, powering the world’s largest hyperscalers with custom chips and high-performance networking solutions.
Hope you enjoy it! And if you do, feel free to share it with friends and fellow investors.
In case you missed it, here are some recent insights:
Subscribe now and never miss a single report:
Our deep dive is divided into 12 sections:
Industry Overview
Broadcom History
Corporate Governance and Directors
Business Model
Main Business Lines
Product Pipeline and Main Clients
Value Proposition
Competitive Advantages
Unit Economics
Valuation
Risks
Investment Thesis
🌐 Industry Overview:
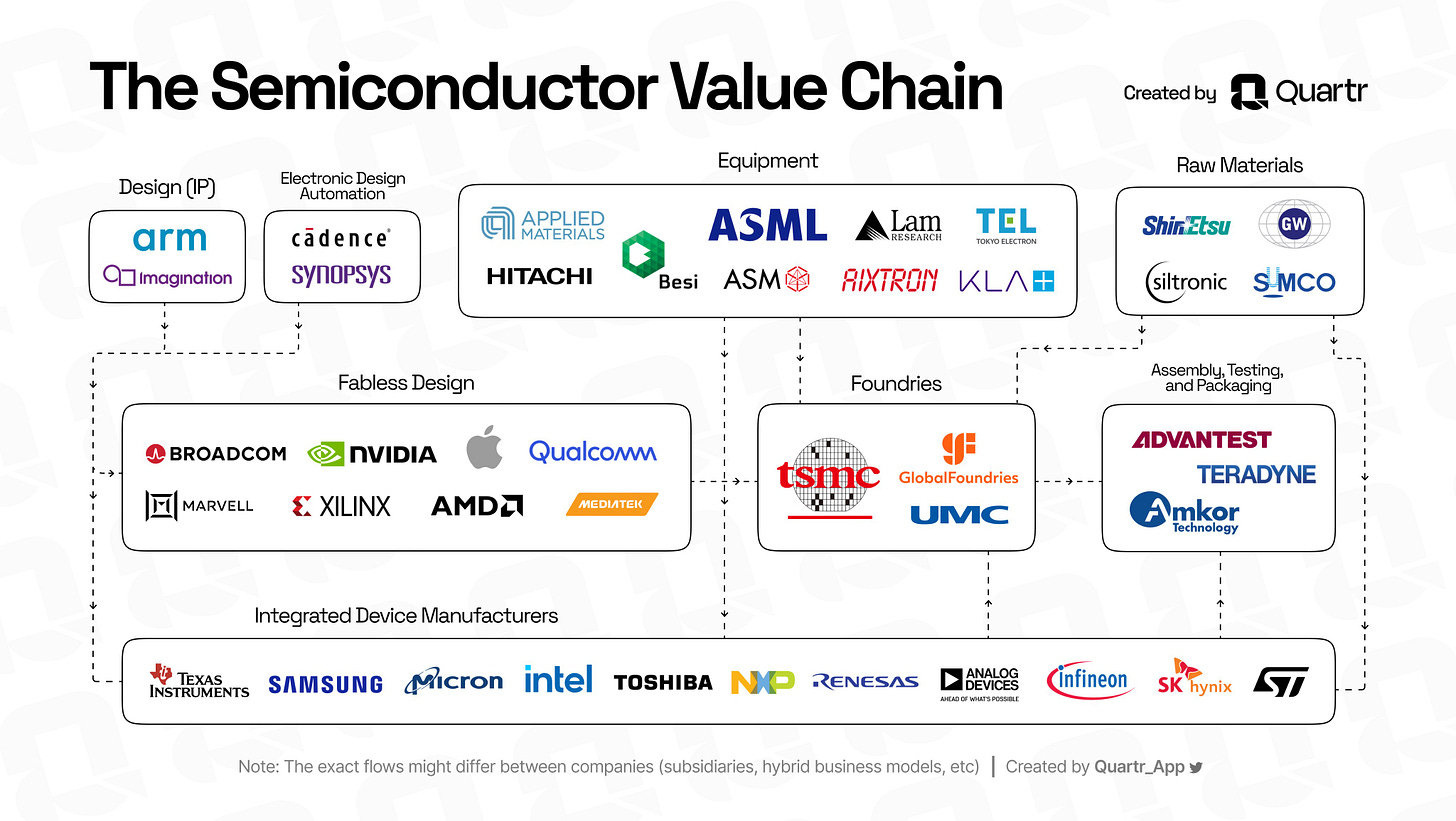
I. Value Chain:
The semiconductor industry is a highly intricate and interconnected ecosystem, where different companies specialize in various stages of chip design, production, and deployment.
“It is better to specialize in what you do best and trade for the rest, rather than trying to do everything yourself.” - David Ricardo (1772-1823)
The value chain includes the following key segments:
Design (IP) and Electronic Design Automation (EDA):
Companies like Arm and Imagination create the intellectual property (IP) that forms the foundation of semiconductor chips.
Cadence and Synopsys provide software tools for designing, simulating, and testing semiconductor components, enabling accurate chip design.
Fabless Design:
Fabless companies like NVIDIA, AMD, Qualcomm, and Broadcom design chips but do not manufacture them.
These companies rely on foundries to fabricate their designs.
Foundries:
Manufacturers like TSMC, GlobalFoundries, and UMC handle the physical fabrication of chips. Broadcom, for example, partners heavily with TSMC for its advanced chips.
Equipment Providers:
Companies such as ASML, Applied Materials, and Lam Research supply the advanced machinery and tools required for semiconductor manufacturing, including lithography and etching.
Raw Materials:
Suppliers like Shin-Etsu and Siltronic provide essential materials such as silicon wafers, which are the foundation of semiconductor fabrication.
Assembly, Testing, and Packaging:
Firms such as Advantest and Amkor Technology handle the final steps, ensuring chips are functional and packaged for use.
Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs):
Companies like Intel, Samsung, and Micron manage both design and manufacturing, integrating multiple stages of the value chain.
II. Future Projections:
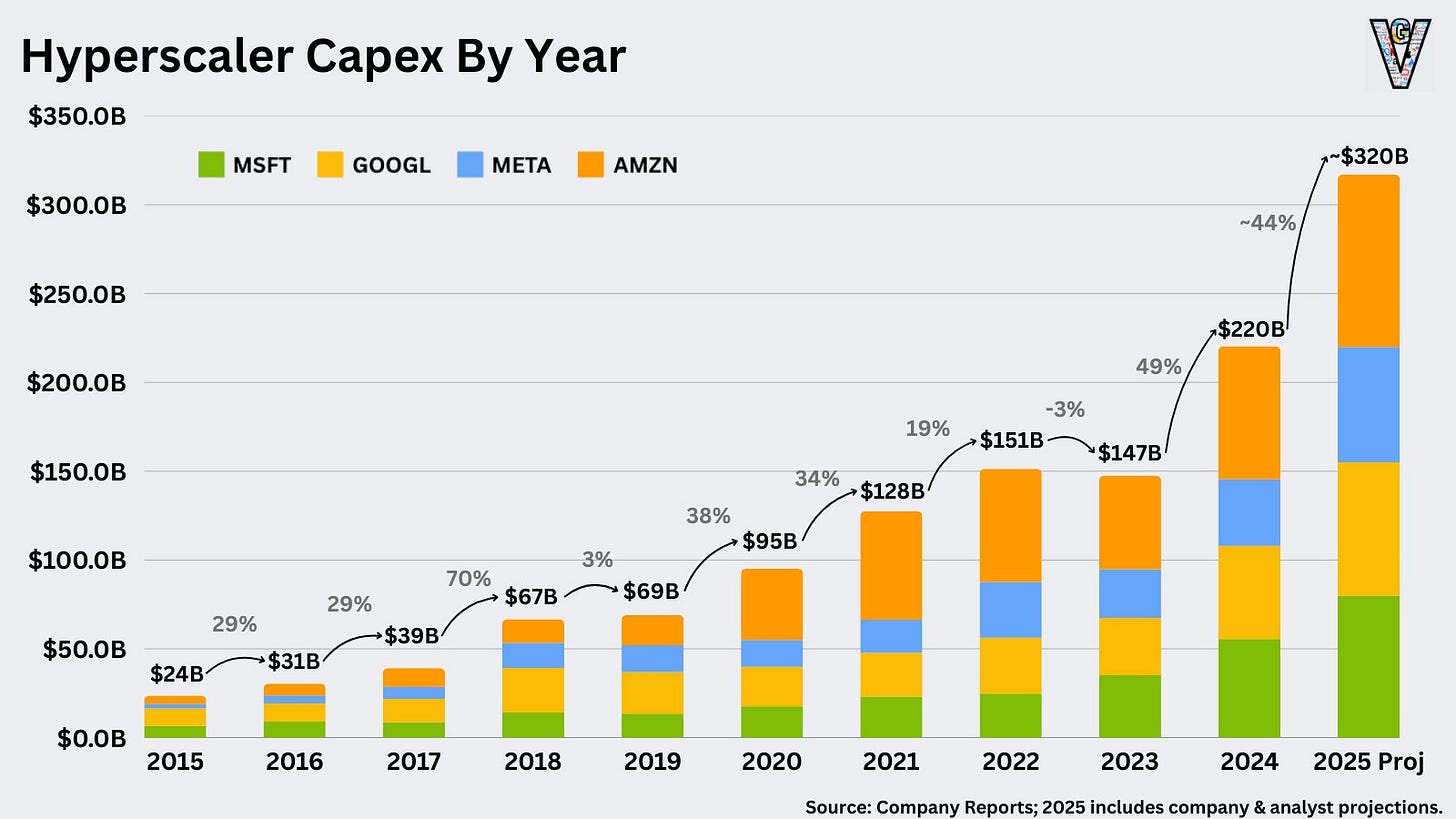
The semiconductor industry is on track for significant expansion, with analysts forecasting the global market to surpass $1 trillion by 2030. This growth is being propelled by the increasing demand for data centers, 5G networks, autonomous vehicles, and IoT devices.
A major driver of this surge is the aggressive capital investment from hyperscalers such as Google, Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta, all competing to develop AI-focused data centers.
Industry estimates indicate that these companies will allocate over $400 billion toward cloud and AI infrastructure through 2027, creating an unprecedented need for high-performance AI chips, custom ASICs, and advanced networking solutions.
The growth ahead will be massive - and Broadcom will play an indispensable role in this story…
Found this content valuable? Share it with your network! Help others discover these insights by sharing the newsletter. Your support makes all the difference!
📖 Broadcom History:
Origins and Early Years:
Broadcom traces its roots back to 1961, when it was established as HP Associates - a semiconductor division of Hewlett-Packard (HP). In 1999, this division spun off with the creation of Agilent Technologies.
The Birth of Avago Technologies:
In 2005, private equity firms KKR and Silver Lake Partners acquired Agilent’s semiconductor business for $2.6 billion, forming Avago Technologies. Avago expanded through acquisitions, including:
2008: Infineon’s bulk acoustic wave business.
2013: LSI Corporation for $6.6 billion, boosting its data center storage solutions.
2014: PLX Technology and Emulex Corporation (2015), further expanding its networking and storage capabilities.
Becoming Broadcom Limited:
The pivotal moment came in 2015, when Avago acquired Broadcom Corporation for $37 billion, creating Broadcom Limited. This merger expanded Broadcom's reach into mobile, IoT, and data center technologies, making it one of the world’s largest semiconductor companies.
Shift to Infrastructure Software:
After a failed attempt to acquire Qualcomm in 2017, blocked by the U.S. government due to national security concerns, Broadcom shifted its growth strategy to enterprise software:
Acquired CA Technologies (2018) for $18.9 billion, entering the mainframe and enterprise software market.
Acquired Symantec’s enterprise security division (2019) for $10.7 billion, expanding into cybersecurity solutions.
From Limited to Inc.:
In 2018, Broadcom moved its legal headquarters from Singapore to the United States and changed its name to Broadcom Inc.
👔 Corporate Governance:
Broadcom’s ownership structure is dominated by large institutional investors. As of 2024, the largest shareholders include The Vanguard Group (10.03%), BlackRock (7.63%), Capital World Investors (4.53%), Capital International Investors (4.04%), and State Street Corporation (3.95%).
Hock Tan serves as Broadcom’s CEO and President, a position he has held since 2006. Born in Malaysia, Tan holds a mechanical engineering degree from MIT and an MBA from Harvard University.
Under his leadership, Broadcom has achieved significant growth through a series of strategic acquisitions and expansion into the semiconductor and software markets. In February 2024, Tan was also appointed to the board of directors at Meta Platforms.
Hock Tan is widely recognized for his focus on operational efficiency, cost discipline, and shareholder returns, which has been central to Broadcom’s growth and profitability.
Enjoying the content? Don’t miss out on more exclusive insights and analyses. Upgrade to paid now and stay updated.
💼 Business Model:
Broadcom ($AVGO) operates a hybrid business model that combines (i) semiconductor solutions with (ii) infrastructure software, creating a powerful synergy between hardware and software capabilities.
Historically, the company was primarily focused on four key segments: Wired Infrastructure, Wireless Communications, Enterprise Storage, and Industrial & Other.
However, as Broadcom expanded its software portfolio through major acquisitions (like CA Technologies, Symantec, and Brocade), it restructured its revenue breakdown into two main segments: Semiconductor Solutions and Infrastructure Software.
I. Semiconductor Solutions:
This segment includes a broad range of products that power essential technologies in wireless communications, data centers, networking, and AI/deep learning.
Broadcom’s chips are integral to smartphones, networking equipment, and enterprise storage, with a particularly strong presence in wireless (where it provides critical components for leading smartphone manufacturers) and networking (where it dominates in datacenter infrastructure and custom AI chips).
II. Infrastructure Software:
This newer segment reflects Broadcom’s strategic move beyond hardware into enterprise software, focusing on security, automation, and cloud-based infrastructure management.
With acquisitions like CA Technologies and Symantec, Broadcom now offers solutions that help businesses manage and secure their IT environments.
📡 Main Business Lines:
I. Wired Infrastructure:
Broadcom is a key provider of semiconductor solutions for broadband, data centers, and networking hardware. These solutions are crucial for enabling high-speed data transmission and connectivity.
Set-Top Box Solutions: chips that power digital video recording, transcoding, and faster channel switching in home entertainment systems.
Broadband Access Solutions: components for modems, routers, and residential gateways that deliver high-speed internet.
Ethernet Switching and Routing: optimized solutions for data centers and service provider networks, offering faster and more reliable data transmission.
II. Wireless Communications:
Broadcom’s wireless solutions enable connectivity for billions of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
RF Semiconductor Devices: industry-leading FBAR filters, enabling mobile devices to support advanced LTE frequency bands.
Connectivity Solutions: wi-fi and bluetooth chipsets, GPS modules, and integrated solutions combining multiple wireless standards.
III. Enterprise Storage Solutions:
Broadcom provides essential components for enterprise storage systems, ensuring secure and efficient data management.
Fibre Channel Switches: acquired from Brocade, these switches deliver high-speed connectivity between servers and storage devices for mission-critical operations.
SAS, RAID, and PCIe Controllers: high-performance solutions for secure data transmission and protection against data loss.
HDD and SSD Solutions: chips that manage data reading, writing, and protection in both traditional hard drives and solid-state drives.
IV. Industrial & Other Solutions:
Broadcom’s industrial solutions support automation, power management, and automotive applications, contributing to advancements in manufacturing and transportation technology.
Optocouplers: provide electrical isolation to protect sensitive signaling systems from interference, used in motors and power systems.
Industrial Fiber Optics: enable high-speed data transfer in factory automation and industrial networking.
Motion Encoders: deliver precise motion control for industrial robots and motors, enhancing efficiency in automated processes.
V: Infrastructure Software:
Broadcom has built a robust enterprise software portfolio through strategic acquisitions, including CA Technologies and Symantec’s enterprise business. These software solutions are vital for IT operations, cybersecurity, and enterprise management.
Mainframe Software Solutions: tools for IBM mainframe platforms, supporting operations for large enterprises.
Agile Planning and DevOps Tools: solutions to streamline software development and improve team collaboration.
Cybersecurity Offerings: security products, including endpoint protection and payment security solutions, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
Found this content valuable? Share it with your network! Help others discover these insights by sharing the newsletter. Your support makes all the difference!
📲 Product Pipeline and Main Clients:
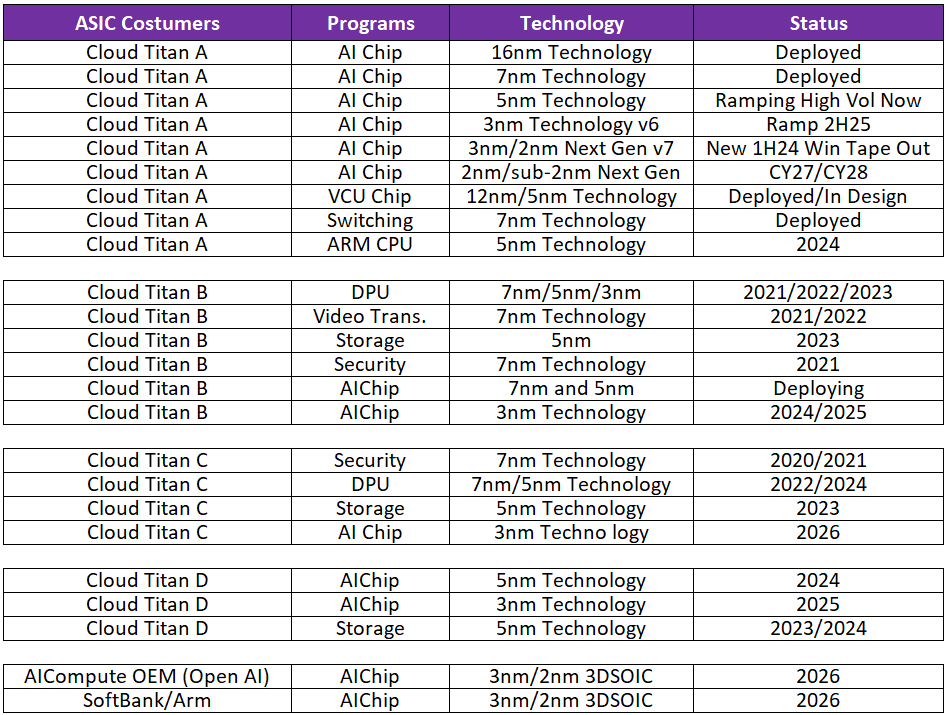
Broadcom is building a powerful pipeline of custom AI chips (ASICs) for some of the world’s largest tech companies.
Currently, it supplies custom chips to Google, Meta, ByteDance, OpenAI, and is now expanding to include SoftBank/ARM as its fifth major AI customer.
Google: Broadcom powers Google’s custom AI chips (TPUs), with next-gen TPU v6 (3nm) launching in 2H 2025 and early work on TPU v7 and v8 already underway. Google is expected to generate over $11 billion in revenue for Broadcom this year.
Meta: Broadcom supplies chips for Meta’s MTIA AI accelerator, with the next-gen 3nm version set to launch in late 2025 and 2026.
OpenAI & SoftBank/ARM: Broadcom is collaborating on AI chips for Project Stargate, SoftBank’s $500B AI initiative. The first 3nm/2nm chips are expected to launch in 2026, supporting SoftBank’s massive data center expansion.
Broadcom’s cutting-edge 3D chip packaging and high-speed I/O (200Gbps) give it a technical edge, driving strong revenue growth from a booming AI market…
🎯 Value Proposition:
I. Tailored Solutions and Hyperscaler Partnerships:
Broadcom sets itself apart by delivering customized, high-performance solutions through long-term collaborations with the world’s largest hyperscalers, including Google and Meta.
Unlike competitors offering off-the-shelf products, Broadcom works side-by-side with its clients to design chips optimized for their unique AI workloads. From semiconductor packaging to system-on-chip (SoC) design, Broadcom’s solutions are built to handle the immense demands of training large language models and running massive inference workloads.
This customized, end-to-end approach translates into higher efficiency and lower costs, providing tangible competitive advantages.
These partnerships go beyond hardware. Broadcom provides:
Custom chip design tailored to each hyperscaler’s AI architecture.
Software integration and system-level validation, ensuring seamless performance within massive data center ecosystems.
On-site engineering resources, allowing Broadcom to co-innovate alongside its customers and quickly adapt to their evolving needs.
With three of the largest hyperscalers planning to deploy up to a million custom AI accelerators each, Broadcom is uniquely positioned to capture a $60 billion to $90 billion market opportunity by 2027.
II. AI Connectivity and Scalable Models:
While many chipmakers focus solely on raw compute power, Broadcom goes further by solving the critical connectivity challenge of AI infrastructure.
As AI models become increasingly complex - potentially reaching tens of trillions of parameters - data centers must connect millions of accelerators into a single, cohesive system.
Broadcom’s advanced Ethernet switching and high-speed interconnect solutions, including the cutting-edge Jericho3-AI switch, are essential for clustering these accelerators efficiently.
By delivering high-bandwidth, low-latency networking at scale, Broadcom provides the infrastructure necessary for the future of AI model training and inference.
Enjoying the content? Don’t miss out on more exclusive insights and analyses. Upgrade to paid now and stay updated.
♟️ Competitive Advantages:
I. Integrated Ecosystem and Comprehensive Product Offering:
Broadcom offers a full-stack technology ecosystem, providing solutions that span from AI chips (ASICs) to networking, storage controllers, DPUs, and security solutions.
This breadth allows Broadcom to address the entire data center infrastructure, making it a one-stop partner for hyperscalers. Customers benefit from seamless integration, higher performance, and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO).
Full-Stack Advantage: Broadcom’s ability to supply both compute (AI ASICs) and connectivity (Ethernet switches) drives cross-product adoption.
Vertical Integration: by providing both custom silicon and critical networking infrastructure, Broadcom increases switching costs and deepens customer reliance.
II. Proprietary Advanced Technology and Engineering Leadership:
Broadcom leads the market with its custom ASIC design capabilities, 3D SOIC advanced packaging, and high-speed I/O solutions (up to 200Gbps/channel). Its 2nm/3nm chiplet reference platform allows customers to integrate best-in-class compute, memory, and networking within a single architecture.
Technical Edge: Broadcom is one of the few companies capable of designing chips with over 100 billion transistors, essential for large-scale AI workloads.
Manufacturing Leadership: partnerships with TSMC ensure access to the latest fabrication nodes (2nm/3nm), keeping Broadcom ahead of technological curves.
Innovation Cycle: proprietary platforms enable faster time-to-market for customers' next-gen AI models (e.g., Google TPU v7, Meta MTIA, SoftBank Izanagi).
III. Deep Customer Relationships and Tailor-Made Solutions:
Broadcom’s success is built on multi-year, co-engineered programs with top hyperscalers. The company’s embedded engineering teams collaborate directly with customers to design customized AI ASICs that address specific workload needs.
High Switching Costs: custom co-design creates long-term lock-in, making it costly and time-consuming for customers to switch to competitors.
Repeat Business: Broadcom consistently wins follow-on programs from its largest customers, such as Google TPU v6, v7, and v8.
Expanding Pipeline: secured multi-generational AI ASIC engagements with SoftBank’s Project Stargate, representing a potential $30 billion opportunity.
IV. Diversified Business Model with Strong AI Exposure:
While Broadcom’s AI business is a major growth driver, it is supported by a diversified portfolio that includes infrastructure software (Symantec, CA Technologies) and networking products (Brocade, Jericho3-AI switches). This diversification provides stability while maintaining exposure to the high-growth AI segment.
AI-Powered Growth: Broadcom’s AI ASIC pipeline, including programs for Google, Meta, OpenAI, and SoftBank, targets a $60–$90 billion addressable market (SAM) by 2027.
Software Recurring Revenue: Broadcom’s infrastructure software portfolio provides stable, recurring cash flows that balance the cyclical nature of hardware sales.
Networking Dominance: market leadership in Ethernet switching (e.g., Jericho3-AI), which is critical for scaling large AI models.
Found this content valuable? Share it with your network! Help others discover these insights by sharing the newsletter. Your support makes all the difference!
📈 Growth Through Aquisitions:
Broadcom’s growth has been driven by a series of bold acquisitions. Since its days as Avago Technologies, the company has followed a clear strategy: buy market leaders with strong technology but inefficient operations.
Broadcom then cuts costs, boosts profitability, and integrates the new business into its broader ecosystem. This approach has helped Broadcom expand into new markets while driving strong margins and cash flow.
Symantec and CA Technologies were the first steps toward an even bigger move: the acquisition of VMware.
In 2023, Broadcom completed its largest deal yet, acquiring VMware for $69 billion - a major leap into enterprise software, adding cloud and virtualization tools to its growing portfolio.
VMware fits perfectly into Broadcom’s ecosystem, complementing its hardware offerings and creating new cross-selling opportunities. It also gives Broadcom more exposure to software, which brings stable, recurring revenue.
With this deal, Broadcom is positioning itself as a full-stack infrastructure provider, from chips to cloud management - while staying true to its playbook of driving profitability through scale and efficiency.
Before we continue...
Thank you for being a valued reader of Jimmy's Journal — your support inspires and empowers me to continue this journey.
If you enjoy Jimmy's Journal, it would mean the world to me if you invited friends to subscribe and read with us. If you refer friends, you will receive benefits that give you special access to Jimmy's Journal.
📢 How to participate:
1. Share Jimmy's Journal. When you use the referral link below, or the “Share” button on any post, you'll get credit for any new subscribers. Simply send the link in a text, email, or share it on social media with friends.
2. Earn benefits. When more friends use your referral link to subscribe (free or paid), you’ll receive special benefits.
Get a 1 month comp for 5 referrals
Get a 3 month comp for 10 referrals
Get a 6 month comp for 15 referrals
To learn more, check out Substack’s FAQ.
Thank you for helping get the word out about Jimmy's Journal!
💹 Unit Economics:
I. Revenues:
Broadcom generates revenue primarily through a mix of long-term contracts, recurring software subscriptions, and spot hardware sales, but its business model has increasingly shifted toward recurring revenue streams, especially after its expansions into software.
Semiconductor Segment: Broadcom sells custom AI chips (ASICs), networking switches, and storage controllers, often through long-term supply agreements (LTAs) with major customers. While hardware sales can include spot purchases, most large deals are structured as multi-year contracts, ensuring stable, recurring revenue.
Software Segment: with acquisitions like CA Technologies, Symantec Enterprise, and VMware, Broadcom has built a significant subscription-based software business. This segment includes enterprise security, mainframe software, and cloud management tools, all delivered through annual or multi-year licensing and SaaS models, generating high-margin recurring revenue.
II. Costs:
Broadcom operates with a highly efficient cost structure, which is largely fixed, enabling significant operating leverage.
The company's ability to maintain gross margins around 70% stems from a combination of technological leadership, economies of scale, and disciplined cost management, particularly through its M&A strategy. Here’s how its cost structure and margin profile work:
R&D and Engineering: as a leader in custom ASICs and networking solutions, Broadcom incurs high upfront R&D costs, particularly for advanced chip designs (e.g., 3nm/2nm ASICs). However, once a chip design is completed, incremental production costs are low, creating strong operating leverage.
Manufacturing: Broadcom is a fabless semiconductor company, outsourcing production to TSMC, which keeps capital expenditures (CAPEX) low. The largest cost components are wafer procurement and assembly/test services, which have high fixed costs but declining unit costs with scale.
Software Operations: the software segment (CA Technologies, Symantec, VMware) operates on a highly scalable model with low variable costs, as software sales and updates are delivered digitally. This segment contributes significantly to Broadcom’s recurring high-margin revenue.
Now, let's dive deep into Broadcom's valuation, analyzing both multiples and a DCF model (with a 2025E target price)…
📊 Valuation:
I. Financial Performance:
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Jimmy's Journal to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.